Electrical conductors are essential components in every electrical system, from industrial plants to commercial buildings. The right choice impacts efficiency, safety, and long-term reliability. This article explores the main types of conductors and specialized applications, helping you make informed decisions for successful electrical projects.
What Are Electrical Conductors?

Electrical conductors are materials that allow electric current to flow through them with minimal resistance. In simple terms, they provide a path for electrons to move from one point to another, enabling the transfer of energy that powers devices, machinery, and entire electrical systems.
The main function of a conductor is to carry electricity efficiently while maintaining system stability. Conductors achieve this by offering a low-resistance path, which minimizes energy loss and prevents excessive heat buildup. Their performance depends on the material, cross-sectional area, and physical construction, all of which influence how much current they can safely carry.
Electrical conductors come in various forms, including solid and stranded wires, cables, busbars, and overhead lines. They can be made from materials like copper, aluminum, or specialized alloys, each chosen based on conductivity, strength, and environmental resistance.
To understand how each type performs and where it is best applied, let’s explore the common conductor materials and their characteristics in detail below.
Common Types of Conductor Materials in Electrical Engineering

Several materials are widely used as conductors, each offering distinct properties that make them suitable for particular applications.
1. Copper
Copper conductors are the most widely used electrical conductors, known for their excellent conductivity and mechanical strength. Their conductivity is approximately 58 MS/m, which allows efficient energy transfer in most electrical systems. Copper is flexible, durable, and resistant to corrosion, making it ideal for both residential and industrial applications.
Pros:
- Excellent electrical conductivity
- High tensile strength and flexibility
- Long service life with minimal maintenance
Cons:
- Higher material cost compared to aluminum
- Heavier, which can increase installation effort
2. Алюминий
Aluminum conductors are lightweight and cost-effective, with conductivity around 36–38 MS/m. They are commonly used in overhead power lines and large-scale power distribution due to their low density and high strength-to-weight ratio.
Pros:
- Lighter than copper, reducing structural support requirements
- Lower cost for large-scale applications
- Good corrosion resistance, especially with protective coatings
Cons:
- Lower conductivity than copper
- More prone to thermal expansion and loosening at joints
- Requires careful installation to avoid damage
3. Silver
Silver conductors provide the highest electrical conductivity of all metals (~63 MS/m), making them suitable for high-frequency circuits, precision instruments, and specialized industrial equipment. Due to cost, silver is often used as plating over copper.
Pros:
- Highest conductivity, excellent for high-performance applications
- Reliable performance under extreme conditions
- Often combined with copper to reduce cost while maintaining conductivity
Cons:
- Very expensive, not practical for general wiring
- Soft metal, less mechanically robust on its own
4. Nickel Plated Copper
Nickel-plated copper conductors combine copper’s excellent conductivity with nickel’s corrosion and heat resistance. They are commonly applied in high-temperature environments, marine applications, and industrial equipment.
Pros:
- Good corrosion and oxidation resistance
- Maintains high conductivity
- Suitable for high-temperature or chemically aggressive environments
Cons:
- Higher cost than plain copper
- Nickel plating adds complexity to manufacturing
5. Нержавеющая сталь
Stainless steel is primarily used in composite or reinforcement conductors due to its high mechanical strength and corrosion resistance, though its conductivity is lower (~1.4 MS/m).
Pros:
- Excellent mechanical strength and durability
- Corrosion-resistant, suitable for harsh environments
- Often used as reinforcement in overhead lines
Cons:
- Low electrical conductivity, unsuitable as primary conductor
- Heavier than aluminum or copper for the same current capacity
6. High-Strength Alloy
High-strength alloy conductors are engineered for applications requiring both durability and sufficient conductivity, often in industrial and high-voltage environments.
Pros:
- High mechanical strength, resistant to stretching
- Maintains reliable conductivity under stress
- Corrosion-resistant, suitable for outdoor or industrial use
Cons:
- Conductivity lower than pure copper or silver
- More expensive than standard aluminum or copper conductors
| Conductor Material | Max Continuous Operating Temperature | Corrosion Resistance | Solderability | Tensile Strength (psi) | Conductivity (%) | Price Level | Weight per Meter (kg) |
| Copper (Cu) | 90°C | Good | Excellent | ~55,000 | 100 | Medium | 0.212 |
| Aluminum (Al) | 75°C | Умеренный | Good | ~40,000 | 61 | Низкий | 0.075 |
| Silver (Ag) | 70°C | Excellent | Excellent | ~40,000 | 105 | Высокий | 0.051 |
| Nickel Plated Copper | 90°C | Excellent | Good | ~55,000 | 100 | Medium | 0.220 |
| Stainless Steel (SS) | 870°C | Excellent | Fair | ~80,000 | 2 | Высокий | 0.150 |
| High Strength Alloy | 200°C | Умеренный | Fair | ~60,000 | 90 | Высокий | 0.180 |
Note: The data above are approximate. If you require further details or have specific questions, feel free to contact us!
Specific Types of Conductor in Overhead Power Transmission
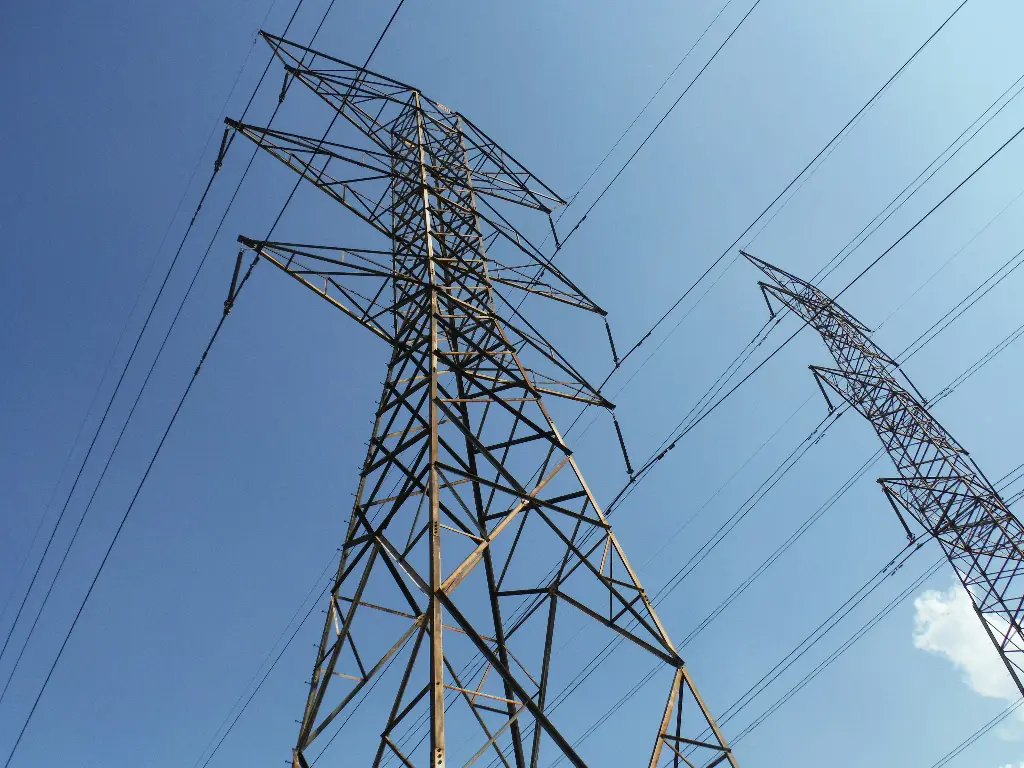

Overhead power transmission requires conductors that can carry high currents over long distances while withstanding mechanical stress, weather, and environmental challenges. Four widely used overhead conductor types are ACSR, AAC, AAAC, and ACAR, each using specific aluminum or aluminum alloy grades to balance conductivity, strength, and durability.
ACSR (Aluminum Conductor Steel Reinforced)

ACSR consists of a galvanized steel core surrounded by layers of 1350-H19 pure aluminum strands, which provide excellent conductivity while the steel core ensures high tensile strength. This combination makes ACSR suitable for long spans and heavy ice or wind loads, where mechanical reliability is critical.
Pros:
- Excellent tensile strength for long transmission spans
- Resistant to sag under heavy loads
- Can handle moderate corrosion when galvanized steel is used
Cons:
- Lower conductivity compared to pure aluminum
- Heavier than other aluminum-based conductors
AAC (All Aluminum Conductor)
AAC is made entirely of 1350-H19 pure aluminum strands, known for their high electrical conductivity (~61% IACS) and good corrosion resistance. Lightweight and easy to handle, AAC is ideal for urban or short-span low- to medium-voltage overhead lines, where mechanical strength requirements are moderate.
Pros:
- Cost-effective for low-voltage distribution
- Easy to install and maintain
- Good corrosion resistance, especially in non-industrial environments
Cons:
- Lower tensile strength compared to ACSR
- Not suitable for long spans or heavy mechanical stress
AAAC (All Aluminum Alloy Conductor)

AAAC uses aluminum alloy strands, typically 1350-H19 or 6201-T81 aluminum alloy, to improve tensile strength and corrosion resistance while maintaining relatively high conductivity. Its high strength-to-weight ratio and durability make it suitable for medium- to high-voltage lines, particularly in polluted or coastal environments.
Pros:
- Durable under harsh environmental conditions
- Lightweight, reducing load on poles and towers
- Suitable for medium- to high-voltage overhead lines
Cons:
- Slightly lower conductivity than AAC
- Higher cost than pure aluminum conductors
ACAR (Aluminum Conductor Alloy Reinforced)
ACAR combines a 6201-T81 aluminum alloy core with 1350-H19 aluminum strands, offering high tensile strength, good conductivity, and reduced weight compared to ACSR. This design is optimized for long-distance, high-voltage transmission lines in challenging environmental conditions.
Pros:
- Can span long distances with minimal sag
- Corrosion-resistant and durable
- Lighter than ACSR for similar mechanical performance
Cons:
- Higher cost than AAC or standard ACSR
- Requires specialized fittings and careful handling
Factors to Consider When Choosing the Right Types of Conductor

Choosing the right conductor material is essential for reliable and efficient electrical systems. Engineers and procurement managers should evaluate multiple factors that affect performance, durability, and installation. Key considerations include:
- Electrical Conductivity: High conductivity reduces energy loss and voltage drop, which is crucial for long transmission lines and high-current industrial applications.
- Mechanical Strength: Conductors must withstand tension, wind, ice, and vibrations. Adequate tensile strength prevents sagging, stretching, or breakage during both installation and operation.
- Corrosion and Environmental Resistance: If a conductor is installed in harsh environments, such as coastal areas, industrial zones, or regions with high humidity, it must resist corrosion to maintain long-term performance.
- Weight: Lighter conductors reduce structural loads on poles and towers, lowering construction costs and simplifying installation.
- Temperature Rating: Conductors must maintain performance at expected operating temperatures, including peak loads, without degrading or losing conductivity.
- Ease of Installation and Handling: Flexibility, compatibility with fittings, and termination options affect labor costs and installation efficiency.
- Compliance with Standards: Materials should meet relevant local and international standards to ensure safety, reliability, and regulatory approval. Commonly referenced standards include: ISO 9001, RoHS / REACH, IEC 60228, IEEE Std 738, ASTM B231/B232/B400/B497, BS 215 / BS EN 50183, etc.
Связаться с нами
At Lxelectrical, we specialize in providing high-quality power cables tailored to your unique needs. Our team can advise on the best conductor type for efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
Reach out to us to discuss your project specifications, request samples, or explore our full range of industrial and specialty cables. With decades of experience supplying projects globally, we ensure you make informed decisions that maximize performance and reliability.










