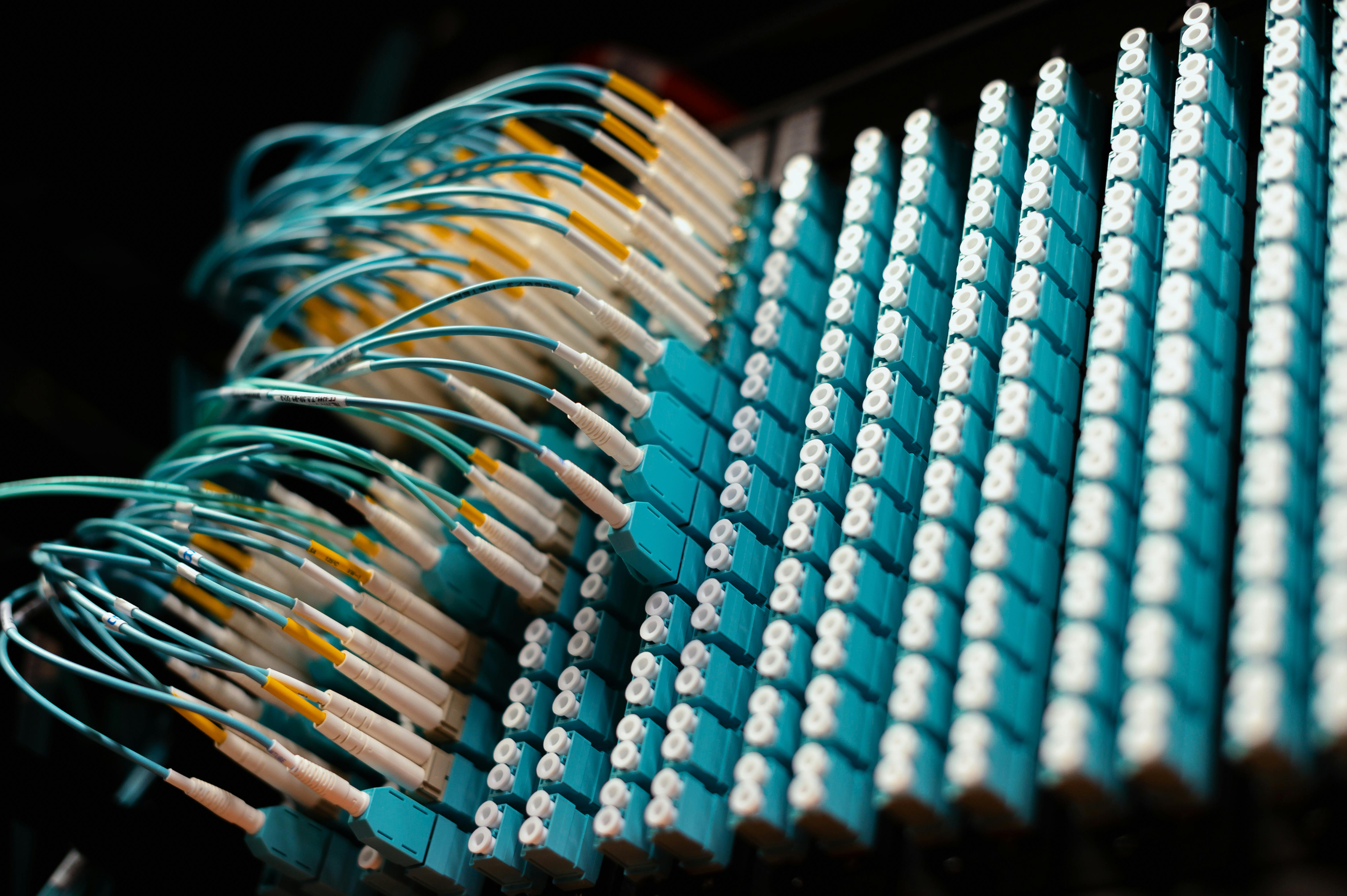
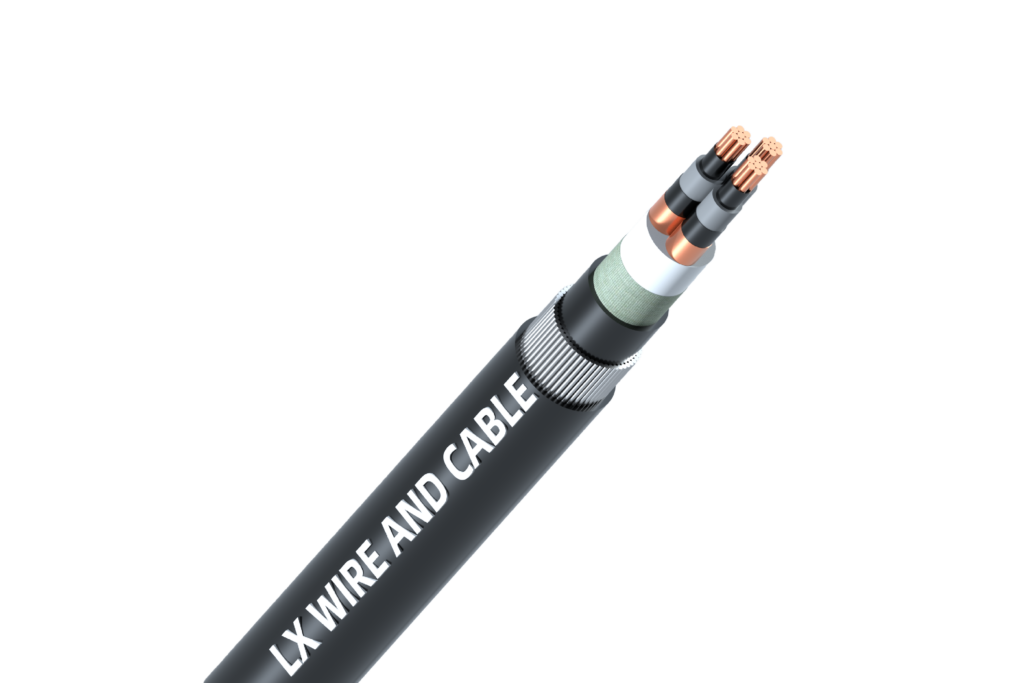
アン 光ファイバーケーブル 光ファイバーは、ガラスやプラスチックの細い線を使ってデータを光信号として伝送する驚異的な技術です。この技術は、電気信号を光に変換し、全反射の原理を利用してケーブル内を伝わることで機能します。
なぜこれが重要なのでしょうか?次の驚くべき事実を考えてみましょう。
- その 世界の光ファイバーケーブル市場 5Gとコネクテッドデバイスの普及により、2024年の$73億から2034年までに$159億に成長すると予想されています。
- 光ファイバーは、信号損失なしに長距離にわたってデータを送信できるため、銅線よりもはるかに効率的です。
- その耐久性により、極端な温度や高湿度などの厳しい環境でも信頼性の高いパフォーマンスが保証されます。
速度、効率、信頼性の組み合わせにより、光ファイバーケーブルは現代の通信システムの基盤となっています。
重要なポイント
- 光ファイバーケーブルは光としてデータを送信し、最大100Gbpsの速度に達します。これは銅線ケーブルよりもはるかに高速です。
- これらのケーブルは強度が高く、水や熱などの過酷な条件にも耐えられます。悪天候でも問題なく動作します。
- 光ファイバーケーブルには、長距離用のシングルモードと短距離用のマルチモードの2種類があり、それぞれ用途が異なります。
- 全反射により光はケーブルコア内に留まります。これによりデータの損失を防ぎ、信号を強力に保ちます。
- 光ファイバーを今すぐ利用すれば、未来への備えができます。より高速で安全、そして快適なインターネット接続を実現します。
光ファイバーケーブルのコンポーネント
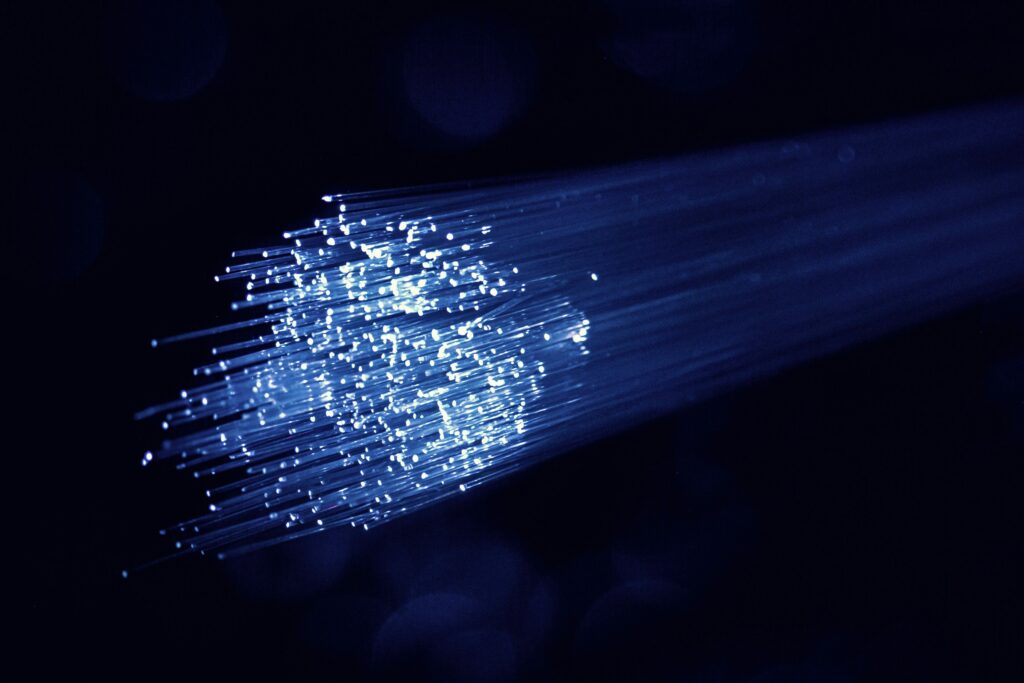
光ファイバーケーブルの構成要素を理解することで、この技術がどのようにして高速データ伝送を実現するかを理解するのに役立ちます。それぞれの部品は、効率、耐久性、信頼性を確保する上で重要な役割を果たします。
コア
コアは光ファイバーケーブルの心臓部です。光信号を伝送するガラスまたはプラスチックの細い線で構成されており、ここからデータ伝送が始まります。コアのサイズによってケーブルの種類(シングルモードかマルチモードか)が決まり、光がどのように伝わるかにも影響します。
コアに使用されている先進的な材料により、効率は大幅に向上しました。例えば、最新のシリカベースの光ファイバーは、信号損失をわずか 0.16 dB/km長距離通信に最適です。損失レベルの内訳は次のとおりです。
| 損失レベル | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 0.5 dB/km | 初期低減により、頻繁な信号再生なしで長距離通信が可能になります。 |
| 0.2 dB/km | シリカベースのファイバーの理論上の限界に近づくさらなる削減。 |
| 0.16 dB/km | 海底および長距離ネットワークにおける超低損失ファイバーの標準。 |
この改善により、長距離でもより高速で信頼性の高い接続を利用できるようになります。
クラッディング
クラッドはコアを囲み、光信号がコア内に留まるようにします。クラッドにはコアよりも屈折率の低い材料が使用されており、全反射の原理が実現されています。このプロセスにより、ケーブルが曲がっても光信号はコア内で反射し、漏れ出すことはありません。
クラッドがないと光信号が散乱し、データ損失につながります。精密な設計により、光ファイバーケーブルは通信用途でもインターネット接続用途でも安定したパフォーマンスを発揮します。
保護層
保護層は、光ファイバーケーブルの繊細な内部部品を環境によるダメージから保護します。これらの層には、ポリマー材料で作られた多層コーティングが含まれており、ケーブルを湿気、極端な温度、物理的ストレスから保護します。
耐久性の向上により、光ファイバーケーブルは過酷な環境下でもより信頼性の高いものとなりました。例えば、 保護コーティング ひび割れや破損を防ぎ、産業用途や屋外用途でも優れた性能を発揮します。詳しくはこちらをご覧ください。
| 証拠の種類 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| 保護コーティング | 繊細なガラス部品を環境要因や物理的損傷から保護する多層ポリマー材料。 |
これらの保護層により、厳しい環境でも光ファイバーケーブルが機能し、効率が維持されます。
光ファイバーケーブルの仕組み
光ファイバーケーブルの仕組みを理解することで、現代の通信におけるその役割をより深く理解することができます。光ファイバーケーブルは、物理原理に基づいて信号の整合性を維持しながら、光を利用して迅速かつ効率的にデータを伝送します。
光透過率
光ファイバーケーブルは、電気信号を光に変換することでデータを伝送します。この光はケーブルのコアを通過し、パルスの形で情報を運びます。電流を使用する従来の銅線とは異なり、光ファイバーケーブルは光を使用することで、はるかに高速な伝送を実現します。
これを理解するために、光ファイバーケーブルと銅線ケーブルの光伝送速度と信頼性の比較を以下に示します。
| 特性 | 光ファイバー | 伝統的な銅 |
|---|---|---|
| 伝送速度 | 最大100Gbps | 最大300Mbps |
| 劣化のない距離 | マイルズ | 数百フィート |
この驚異的な速度と長距離伝送能力により、光ファイバーケーブルはインターネット接続や電気通信などの用途に最適です。
全反射
の原則 全反射 光信号がケーブルのコア内に閉じ込められることを保証します。光がガラスやプラスチックのコアなどの密度の高い媒体を通過し、臨界角よりも大きな角度で境界に当たると、光は完全にコア内に戻ります。このプロセスにより、光が漏れ出すのを防ぎ、信号は損なわれません。
この原理は信号の完全性を維持するために不可欠です。これがなければ、光は散乱し、重大なデータ損失につながります。全反射により、光ファイバーケーブルは干渉を最小限に抑えながら長距離データを伝送することができ、高い信頼性と効率性を実現します。
コンポーネントの役割
光ファイバーケーブルの各コンポーネントは、スムーズなデータ伝送を実現するためにそれぞれの役割を担っています。コアは光信号の経路として機能し、クラッドはコアを囲み、全反射を促進します。保護層はこれらの繊細なコンポーネントを環境によるダメージから保護し、耐久性と安定した性能を確保します。
例えば、クラッドの屈折率はコアよりも低いため、光は内部に閉じ込められます。一方、保護層は物理的な損傷を防ぎ、過酷な環境下でもケーブルの信頼性を確保します。これらのコンポーネントがシームレスに連携することで、光ファイバーケーブルならではの高速・長距離データ伝送を実現します。
光ファイバーケーブルの種類
光ファイバーケーブルはすべて同じではありません。主にシングルモードとマルチモードの2種類があり、それぞれに独自の特性があり、特定の用途に適しています。
シングルモードケーブル
シングルモードケーブルは長距離データ伝送用に設計されており、 コア径通常約10ミクロンの細線で、ケーブルを通過する光モードは1つだけです。この設計により、信号の歪みが最小限に抑えられ、長距離でもデータの完全性が確保されます。
知っていましたか? シングルモードファイバーは、 V数カットオフが2.405未満つまり、基本モードのみが伝播できることになります。
これらのケーブルは、高速データを何マイルも伝送する際に劣化なく伝送する必要がある通信やインターネットバックボーンなどの用途に最適です。また、細いコアは干渉を低減するため、重要な通信システムにおいて高い信頼性を実現します。
マルチモードケーブル
一方、マルチモードケーブルは短距離に適しています。コア径が大きく、通常50~62.5ミクロン程度であるため、複数の光モードが同時に伝搬します。この特性によりケーブルの帯域幅は広がりますが、モード分散の影響で有効範囲が制限されます。
以下に 2 つのタイプを簡単に比較します。
| 繊維の種類 | コア径 | 帯域幅(MHz-km) | 最大距離(m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| マルチモード | 62.5ミクロン | 160 | 220 |
| シングルモード | 10ミクロン | 該当なし | かなり長い |
マルチモード光ファイバーは、波長1.5ミクロン、コア径50ミクロンの場合、V値40.8で示されるように、約832種類の導波モードをサポートできます。この特性により、マルチモード光ファイバーは、短距離で高いデータレートが求められるローカルエリアネットワーク(LAN)やデータセンターなどのアプリケーションに適しています。
どちらのタイプの光ファイバーケーブルも、現代の通信において重要な役割を果たしています。適切なケーブルを選ぶには、距離、帯域幅、用途など、お客様の具体的なニーズに応じて判断してください。
光ファイバーケーブルの利点
高速
速度に関しては、光ファイバーケーブルは従来の銅線ケーブルをはるかに上回ります。光ファイバーケーブルはデータを光信号として伝送するため、ほぼ光速で情報を伝送できます。つまり、大容量ファイルのダウンロード、高解像度動画のストリーミング、ビデオ会議への参加など、遅延なく行うことができます。
おもしろい事実: 1 本の光ファイバー ケーブルで最大 100 Gbps の速度をサポートできるため、現代の高速インターネットの基盤となっています。
この驚異的な速度により、ピーク時でも遅延を最小限に抑えることができます。ゲーム、リモートワーク、あるいは単なるブラウジングなど、光ファイバーケーブルは高速かつ効率的な接続を維持します。
より広い帯域幅
光ファイバーケーブルは、他の種類のケーブルに比べて大幅に広い帯域幅を提供します。帯域幅とは、一度に送信できるデータ量を指します。光ファイバーを使用すれば、パフォーマンスを犠牲にすることなく、大量のデータを同時に送受信できます。
例えば、1本の光ファイバーケーブルで、複数の高解像度ビデオストリーム、オンラインゲームセッション、ファイル転送を同時に処理できます。そのため、大容量ネットワークを必要とする家庭、企業、データセンターに最適です。
| 特徴 | 光ファイバーケーブル | 銅ケーブル |
|---|---|---|
| 最大帯域幅 | 事実上無制限 | 限定 |
| データ転送 | 同時 | 一連 |
この比類のない容量により、データ需要が増大し続けても、ネットワークが将来にも対応できるようになります。
信頼性
信頼性は光ファイバーケーブルのもう一つの重要な利点です。銅線とは異なり、データ伝送を妨害する可能性のある電磁干渉の影響を受けないため、電子機器の重量が重い環境や無線周波数干渉レベルが高い環境に最適です。
さらに、光ファイバーケーブルは物理的な損傷を受けにくいという特徴があります。保護層が湿気、温度変化、さらには厳しい気象条件からもケーブルを保護します。この耐久性により、過酷な環境下でも安定した接続が確保され、途切れることはありません。
ヒント: 医療や金融取引などの重要なアプリケーションで信頼性の高い接続が必要な場合は、光ファイバーケーブルが最適です。
その信頼性により、ダウンタイムやデータ損失が許容されない業界にとって信頼できるソリューションとなります。
耐久性
耐久性という点では、光ファイバーケーブルは現代の通信システムにとって信頼できる選択肢として際立っています。これらのケーブルは過酷な条件にも耐えられるように設計されており、長期にわたって安定した性能を保証します。
光ファイバーケーブルの耐久性を支える重要な要素の一つは、保護層です。これらの層は、繊細なガラスまたはプラスチックのコアを、湿気、極端な温度、紫外線などの環境要因から保護します。例えば、外側のジャケットは、多くの場合、丈夫なポリマー素材で作られており、水の浸入を防ぎ、ケーブルを損傷するのを防ぎます。
ヒント: 天候が予測できない地域に住んでいる場合、光ファイバーケーブルは嵐や熱波の際にも安定した接続を提供します。
光ファイバーケーブルのもう一つの利点は、物理的なストレスに対する耐性です。簡単に曲げたり破損したりする銅線とは異なり、光ファイバーは曲げや伸縮にも耐えられるよう設計されており、信号品質を損なうことはありません。この柔軟性により、狭いスペースや動きの激しい場所への設置に最適です。
以下に、耐久性の面で光ファイバーケーブルと従来の銅ケーブルを比較して簡単に説明します。
| 特徴 | 光ファイバーケーブル | 銅ケーブル |
|---|---|---|
| 耐湿性 | 高い | 低い |
| 耐腐食性 | 高い | 低い |
| 柔軟性 | 高い | 適度 |
さらに、光ファイバーケーブルは電磁干渉(EMI)の影響を受けません。つまり、電子機器や電力線の近くに設置しても性能が低下することはありません。
光ファイバーケーブルをお選びいただくことで、データ伝送ニーズを満たす、長期にわたる信頼性の高いソリューションを確実にご提供いたします。家庭用、業務用、産業用を問わず、その耐久性は賢明な投資となります。
光ファイバーケーブルの用途

光ファイバーケーブルは革命を起こした 様々な より高速で信頼性が高く、効率的なデータ伝送を可能にすることで、産業に貢献しています。その独自の特性により、電気通信、インターネット接続、医療機器などの分野では欠かせない存在となっています。
通信
通信は、比類のない速度と容量を誇る光ファイバーケーブルに大きく依存しています。これらのケーブルは、 10~40 Gbit/s長距離にわたるシームレスな通信を実現します。波長分割多重(WDM)により、1本の光ファイバーで最大80個の独立したチャネルを伝送できるため、ネットワーク容量が大幅に向上します。
おもしろい事実: シングルモード光ファイバーケーブルは、信号劣化なしに数百キロメートルにわたって延長できるため、長距離通信に最適です。
通信業界では、拡張性と耐久性に優れた光ファイバーケーブルの使用を拡大し続けています。 鋼鉄装甲光ファイバーケーブル例えば、過酷な条件にも耐え、極限の環境下でも中断のないサービスを保証します。この信頼性により、修理コストが削減され、堅牢なITソリューションに対する高まる需要に対応できます。
インターネット接続
光ファイバーケーブルは超高速通信を実現することでインターネット接続に革命をもたらしました。米国では ダウンロード速度の中央値は290Mbpsを超えています一部の光ファイバープロバイダーは最大10Gbpsの接続速度を提供しています。この速度により、スムーズなストリーミング、ゲーム、リモートワーク体験が保証されます。
ヒント: ファイバー インフラストラクチャによりインターネット速度が大幅に向上し、住宅ユーザーと商業ユーザーの両方にとって好ましい選択肢となっています。
光ファイバー・トゥ・ザ・ホーム市場は、2025年から2030年にかけて12.2%の複合年間成長率(CAGR)で成長すると予測されています。この成長は、日常生活やビジネス活動における高速インターネットへの依存度の高まりを反映しています。光ファイバーケーブルは、複数のデバイスと高解像度コンテンツを同時にサポートするために必要な帯域幅を提供します。
医療機器
医療分野において、光ファイバーケーブルは医療技術の進歩に重要な役割を果たしています。低侵襲手術、内視鏡画像診断、レーザー治療に不可欠な存在です。医療用光ファイバー市場は、今後20年間で100億ドルから200億ドルの成長が見込まれています。 2021年の1TP5兆12億7千万から2032年までに1TP5兆25億3千万へ外科用器具の革新とヘルスケア投資によって推進されています。
知っていましたか? このセグメントは、2021 年の光ファイバー市場全体の約 26% を占め、医療用途におけるその重要性を浮き彫りにしました。
ヨーロッパや東アジアなどの地域では、医療費の増加とイノベーションの進展により、光ファイバーベースの医療機器の導入が進んでいます。光ファイバーケーブルは、重要な処置における精度と信頼性を確保するため、現代医療に不可欠な存在となっています。
産業用途
光ファイバーケーブルは、その速度、信頼性、そして耐久性から、産業用途において不可欠な存在となっています。これらのケーブルは、高性能なデータ伝送が求められる分野における重要な業務を支えています。製造業、航空宇宙産業、エネルギー産業など、精度と効率性が極めて重要な産業で活用されています。
産業分野における光ファイバーケーブルの大きな利点の一つは、過酷な環境への耐性です。保護層は湿気、極端な温度、物理的ストレスに耐えるため、工場、石油掘削装置、屋外設備などに最適です。例えば、製造工場では、光ファイバーケーブルが自動化された機械を接続し、システム間のシームレスな通信を確保します。これにより、生産性が向上し、ダウンタイムが削減されます。
MPO光ファイバーコネクタ市場分析では、様々な産業分野における光ファイバーケーブルの利用増加が浮き彫りになっています。主な分析結果は以下の通りです。
- 光ファイバーケーブルを利用する主要分野としては、通信、データセンター、軍事/航空宇宙などがあります。
- 市場は 2024年の約7億3000万米ドルから2033年までに23億3000万米ドルに成長すると予測されている。.
- この成長は、産業用アプリケーションにおける高速で信頼性の高いデータ伝送の需要の増加を反映しています。
エネルギー分野では、光ファイバーケーブルは電力網の監視と制御において重要な役割を果たしています。センサーから制御センターへリアルタイムデータを伝送することで、システムの安定性を維持し、停電を防止します。同様に、航空宇宙分野では、これらのケーブルは航空機の高度な通信システムを支え、安全性と効率性を確保しています。
光ファイバーケーブルを使用することで、産業界はデータ転送の高速化、信頼性の向上、メンテナンスコストの削減を実現できます。工場の管理や過酷な環境での運用など、あらゆる場面で、これらのケーブルは、常に先を行くために必要な性能と耐久性を提供します。
光ファイバーケーブルは、比類のない速度、信頼性、そして汎用性を提供することで、データ伝送に革命をもたらしました。これらのケーブルは、速度からメンテナンスコストまで、あらゆる主要な指標において従来の銅線ネットワークを凌駕します。
| アドバンテージ | 光ファイバー技術 | 銅線ネットワーク |
|---|---|---|
| 信頼性 | より高い | より低い |
| 安全 | 改善された | 標準 |
| スピード | もっと早く | もっとゆっくり |
| メンテナンス費用 | より低い | より高い |
| 将来の拡張 | フレキシブル | 限定 |
この技術は、通信、医療、製造業といった産業の発展に重要な役割を果たしています。 遅延、パケット損失、帯域幅 優れた性能を発揮します。光ファイバーケーブルを採用することで、より高速で安全な、将来を見据えた接続を実現できます。
ヒント: 今日光ファイバー技術に投資することで、明日のデジタル世界の増大する需要に備えることができます。
光ファイバーケーブルのニーズにワンストップソリューション
LX CABLEでは、包括的なサービスの一環として、高性能光ファイバーケーブルの提供を専門としています。 ワンストップソリューション 電力伝送と通信のニーズに応える製品を提供しています。20年以上の業界経験に基づき、当社の製品は150カ国以上で信頼されています。高品質なケーブルだけでなく、電力接続金具、絶縁体、工具などの必須アクセサリも取り揃えており、スムーズなプロジェクト遂行を実現します。ISO9001、CE、ROHS、TUV認証を取得し、品質と革新に尽力し、グローバルな接続性を促進する信頼性の高いソリューションを提供しています。
よくある質問
光ファイバーケーブルは、ほぼ光速で移動する光信号としてデータを伝送します。銅線ケーブルは電気信号を使用しますが、電気信号はより遅く、距離が離れるにつれて劣化します。光ファイバーは、より高速で信頼性の高いデータ伝送を実現します。
はい、光ファイバーケーブルは過酷な環境にも耐えられるように設計されています。保護層は湿気、極端な温度、紫外線にも耐えます。この耐久性により、屋外設置や産業用途に最適です。
はい、その通りです!光ファイバーケーブルは電磁干渉の影響を受けにくく、盗聴も検知されにくいため、機密データの伝送において最も安全な選択肢の一つとなっています。
長距離通信にはシングルモードケーブル、短距離通信にはマルチモードケーブルをお選びください。シングルモードは長距離通信において高い信頼性を提供し、マルチモードはデータセンターなどのローカルネットワークにおいてより広い帯域幅を提供します。
光ファイバーケーブルはメンテナンスがほとんど必要ありません。耐久性と環境耐性に優れているため、損傷のリスクを軽減できます。定期的な点検により最適なパフォーマンスを確保できますが、銅線ケーブルに比べて摩耗がはるかに少ないのも特徴です。